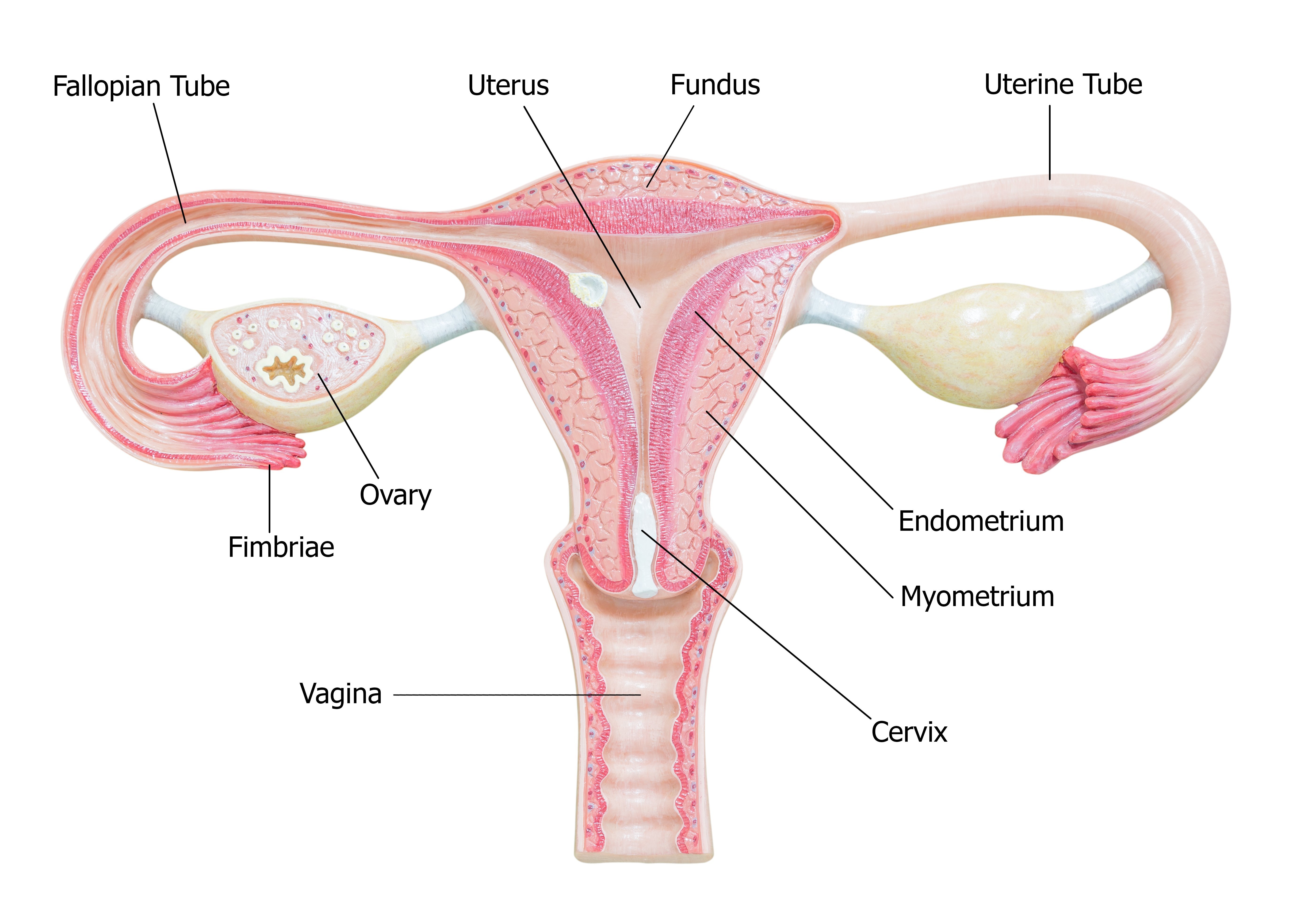
Describe the Structure and Function of the Uterus
Describe the structure and location of the ovaries. Explain the development of an ovarian follicle from the primary follicle to the corpus luteum.
Antenatal Care Module 3 Anatomy And Physiology Of The Female Reproductive System View As Single Page
Paired glands weighing about 3g each resemble large almonds attached to ligaments in pelvic cavity on each side of the uterus.
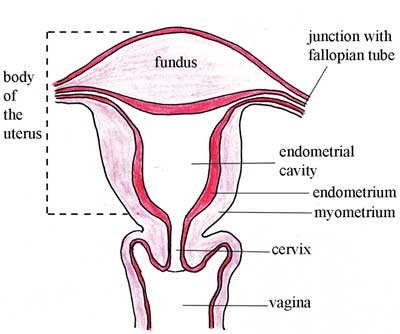
. The cervix which is the lower part that opens into the vagina and the main body of the uterus called the corpus. It supports the developing embryo and fetus during gestation. Learn about the function of the uterus and uterine wall the three layers of the uterus perimetrium.
Iii Uterus - It nurturing the fertilized ovum that develops into the fetus and holding and supporting it till the baby is mature enough for birthb Placenta is a disc which is embedded in the uterine wall. The uterus has three main functions. It is hormonally responsive.
Placenta is a temporary membrane that connects the foetus and the mother mechanically and physiologically to provide nutrition help in respiration and excretion. It is part of the female reproductive system. The fimbriae of the uterine tube also known as fimbriae tubae are small fingerlike projections at the end of the fallopian tubes through which.
Its where an egg is fertilized and a baby grows. Fundus top of the uterus above the entry point of the uterine tubes. The corpus can easily expand to hold a developing baby.
The oviduct provide the place for fertilisation to occur. Produces vaginal and uterine secretions. A small sensitive and elongated erectile organ at the anterior part of the vulva in female mammals homologous with the penis.
While its anatomy sounds simple its histology is more complicated. It is the site of nourishment for the growing baby making it one of the most important reproductive organs in the female body. They transport eggs to the uterus.
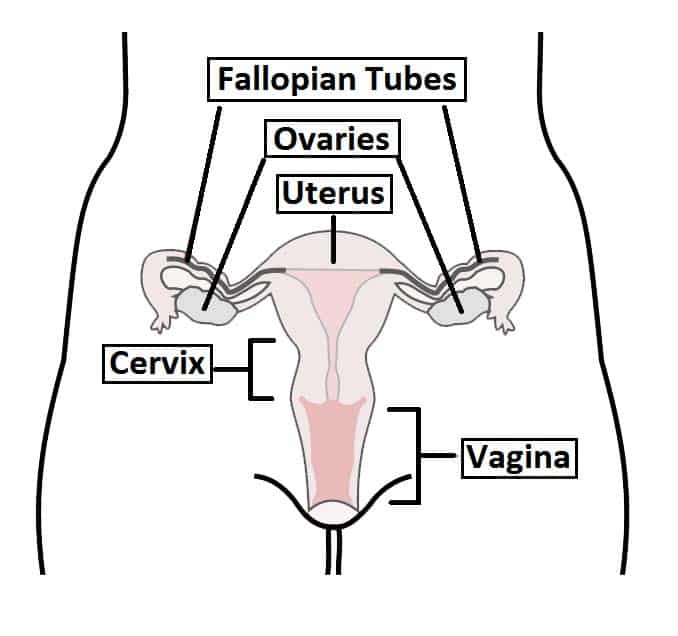
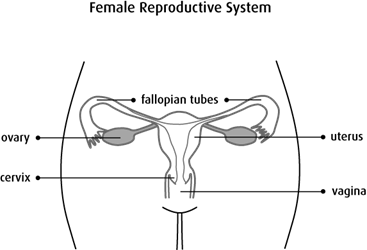
Body usual site for implantation of the blastocyst. It is connected distally to the vagina and laterally to the uterine tubes. An females internal reproductive organs are the vagina uterus fallopian tubes cervix and ovary.
The uterus is a hollow pear-shaped organ that is the home to a developing fetus. Function of the Uterus. The vaginal opening to the uterus.
The uterus is divided into three parts the first part is the cervix which is the lower part that opens into the vagina and the second part is the main body of the uterus which called the corpus the body the corpus can easily expand to hold a developing baby and the fundus which is domed upper portion. The cervix is the lowermost portion of the uterus. External structures include the mons pubis pudendal cleft labia majora and minora vulva Bartholins gland and the clitoris.
The uterus plays a major role in reproductive physiology. Uterus also called womb an inverted pear-shaped muscular organ of the female reproductive system located between the bladder and the rectum. It is about the size of a fist.
These ligaments are attached in turn to the bones of the pelvis. The structure of the cervix is integral to the maintenance of pregnancy keeping the developing baby in utero and forming a barrier to the ascent of microorganisms from the vagina. Passes the anatomically male sperm through to the fallopian tube.
It consists of several anatomical parts such as the cervix isthmus and body. Cervix protrudes into the vagina whereas the uterus is held in position by l View the full answer. They are sufficiently elastic to allow them to stretch considerably during pregnancy and then return to their former size afterwards.
It functions to nourish and house a fertilized egg until the fetus or offspring is ready to be delivered. Perhaps the principal albeit lofty function of the uterus is to preserve life. The uterus consists of a body and a cervix.
Hosts the developing fetus. The uterus is an organ. The uterus has three parts.
Uterus It is the largest organ of the female reproductive system and is the site of fetal growth. The vagina extends from the uterus and ends in the. Extend from the uterus in the lower abdominal cavity to the ovaries but they are not in contact with the ovaries.
The uterus is a female reproductive organ that is essential for proper fetal development. The uterus also commonly known as the womb is a hollow muscular organ of the female reproductive system that is responsible for the development of the embryo and fetus during pregnancy. The uterus and cervix sit centrally in the pelvis at the top of the vagina supported by strong fibrous structures called ligaments.
The first function is to house and provide a nourishing environment for the implanted embryo. The uterus is hollow and pear-shaped. Weakness of the cervix may lead to deficiency of this barrier and is associated with subsequent preterm birth.
The uterus which hosts the developing fetus produces vaginal and uterine secretions and passes. An incredibly distensible organ the uterus can expand during pregnancy from around the size of a closed fist to become large enough to hold a full term baby. You may know it as the womb.
It is associated with the viviparity of the organism. The uterus also known as the womb is an about 8 cm long hollow muscular organ in the female pelvis and lies dorsocranially on the bladder. Oviducts or Fallopian tubes.
Ii Oviduct - Carries the mature egg to the uterus. Its in your lower belly pelvic area. Numerous studies have shown that estradiol and progesterone exert their effects by binding to receptors within the cytoplasm of uterine cells and translocating these receptors to the nuclei where they presumably alter genomic activity.
- protect and activate sperm fructose - facilitate sperm movement fructose - neutralize acidity of sperm and vagina alkaline fluid - decrease viscosity of mucous in cervix prostaglandins - stimulate reverse peristalsis in uterus prostaglandins - suppress female immune response - destroy some bacteria antibiotic chemicals. The uterus plays a major role in reproductive physiology. The uterus is divided into two parts.
Sexual intercourse receives the penis and ejaculate assisting in its transport to the uterus. A structure about the size of a womans fist. It has several roles within the female reproductive system.
The uterus is a thick-walled muscular organ capable of expansion to accommodate a growing fetus. This all begins when an egg or ovum is fertilized by a sperm and will make its downward trek in search of a. It is a distensible muscular tube which extends posterosuperiorly from the external vaginal orifice to the cervix.
The female reproductive system contains two main parts. The placenta in humans is chorionic as it is made of the chorion membrane of extra-embryonic membrane.

Uterus Anatomy Definition Function Location Biology Dictionary

Structures Of The Female Reproductive System Ck 12 Foundation
The Female Reproductive System Structure And Function Nursing Part 1
Uterus Anatomy Definition And Function Human Anatomy Kenhub Youtube

26 5c Uterus Medicine Libretexts
The Uterus Structure Location Vasculature Teachmeanatomy
The Uterus Structure Function And Common Problems Family Doctor
The Uterus Canadian Cancer Society
The Female Reproductive System Structure And Function Nursing Part 1

Uterus An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
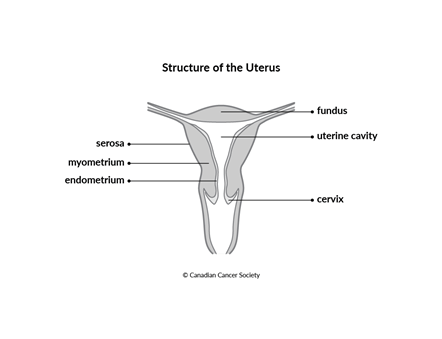
The Uterus Canadian Cancer Society
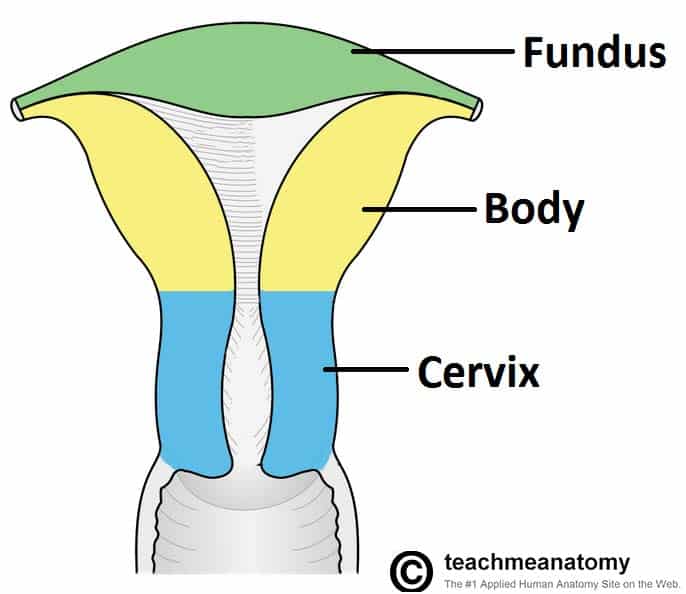
The Uterus Structure Location Vasculature Teachmeanatomy
Anatomy Of The Female Reproductive System

Uterus Definition Function Anatomy Britannica

Cervix Definition Function Location Diagram Facts Britannica
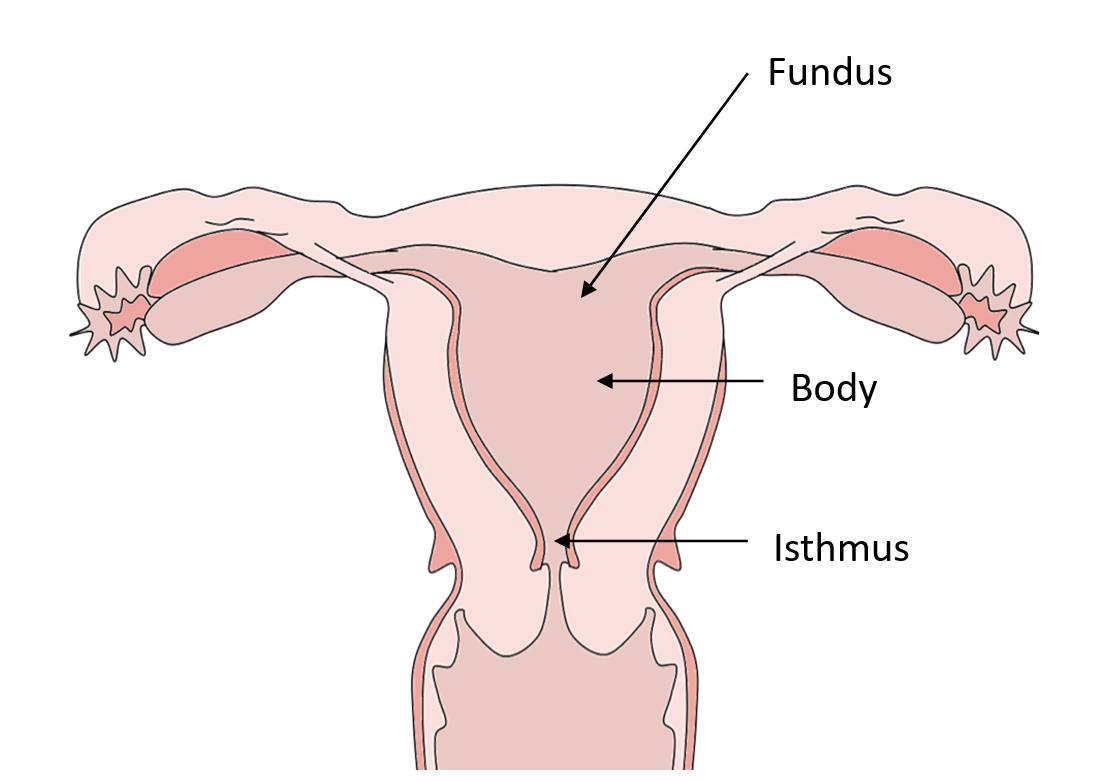
Anatomy Of The Uterus Female Reproductive Anatomy Geeky Medics
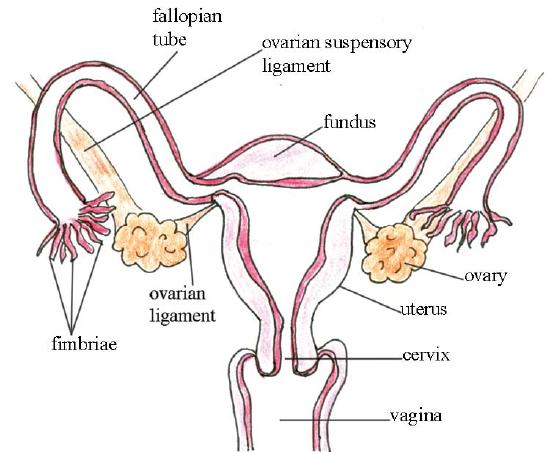
22 6 Structures Of The Female Reproductive System Biology Libretexts

Comments
Post a Comment